38 atp molecule with labels
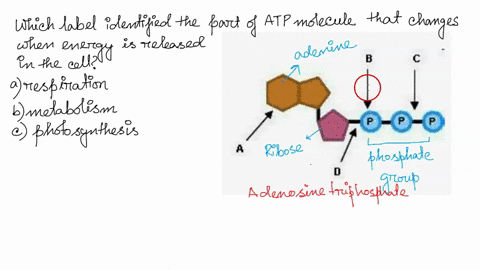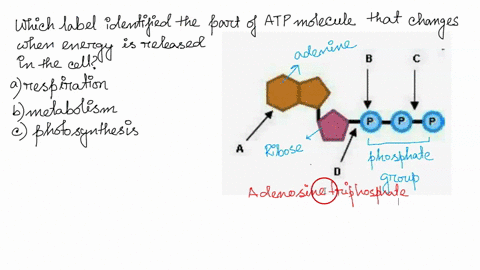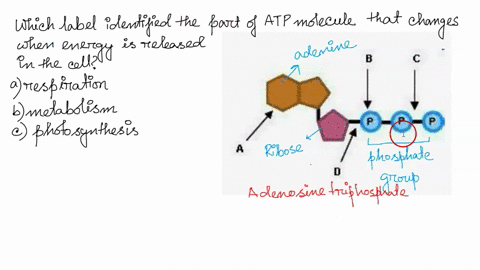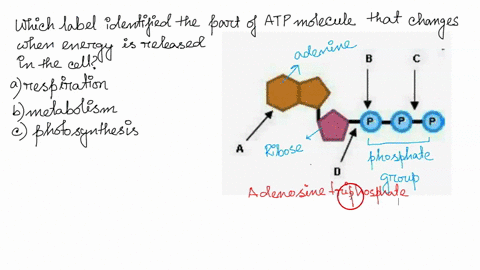
Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Explanation: Cellular respiration is the process by which nutrients such as glucose are broken down using oxygen to generate energy in the form of ATP, that is used to drive cellular processes. ATP consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups in a row. Energ Get more Answers for FREE Insights into the client protein release mechanism of the ATP ... May 20, 2022 · How ATP-independent chaperones release their clients without energy input remains enigmatic. ... Spy is a cradle-shaped molecule with an overall ... we found that all the MTSL spin labels around ...
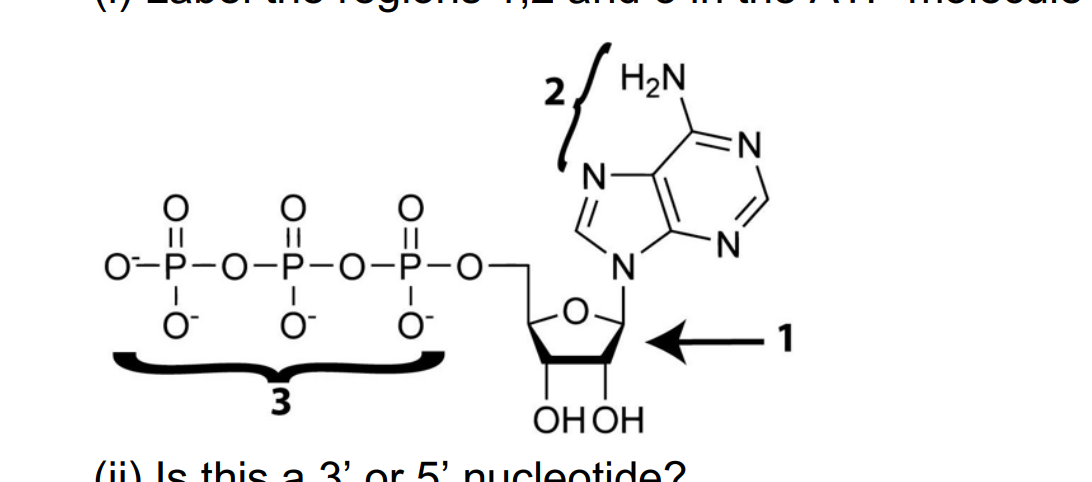
Nucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group. With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleo side mono phosphate", "nucleoside di phosphate" or "nucleoside tri phosphate", depending on how ...
Atp molecule with labels
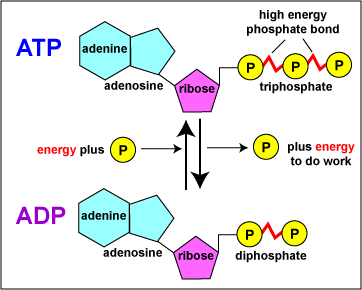
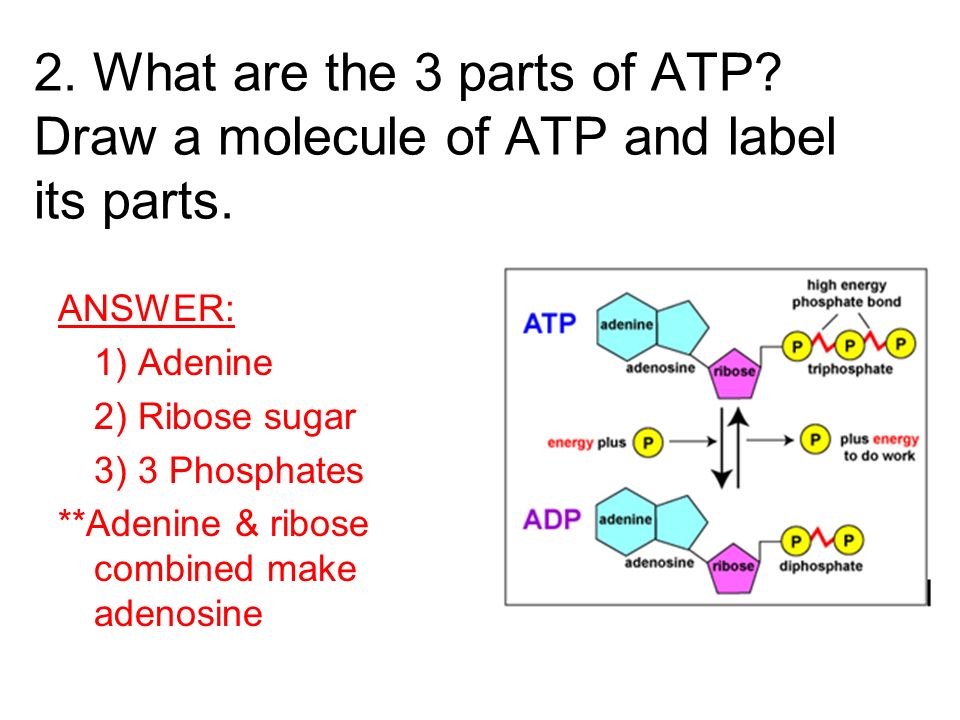
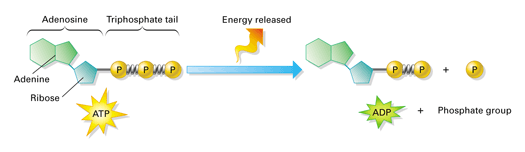
How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com The molecular structure of ATP is comprised of: 1 adenine: A purine base. 1 ribose: A 5-carbon simple sugar. 3 phosphate molecules: The majority of the ATP's energy is also stored within its ... Photosynthesis Flashcards | Quizlet The electron from a molecule of water goes with H+ to the ATP Synthase, to which it joins the sugar G3P. Describe how ATP is produced in the light reactions. A electron goes through PSII then goes to the cytochrome complex then to PSI to which it goes to the ATP synthase. ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College Usually the terminal phosphate is not simply removed, but instead is attached to another molecule. This process is known as phosphorylation. W + ATP -----> W~P + ADP where W is any compound, for example: glucose + ATP -----> glucose~P + ADP. Glucose can be converted into Glucose-6-phosphate by the addition of the phosphate group from ATP.
Atp molecule with labels. Mastering Biology 5 Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the labels onto the table to indicate when each statement is true. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. 1. Orange dye moves independently of purple dye 2. Concentration gradients exist that drive diffusion of both dyes 3. There is a net movement of orange dye from side A to side B 4. Purple dye moves only from side B to ... Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - HHMI BioInteractive Description This model shows the structure of ATP, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. ATP has many important roles in the cell. A major role of ATP is to bind to and activate enzymes called kinases. Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and... RCSB PDB - ATP Ligand Summary Page An adenine nucleotide containing three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety. In addition to its crucial roles in metabolism adenosine triphosphate is a neurotransmitter. Synonyms. Adenosine triphosphate disodium trihydrate. ATP. Adenosine triphosphate. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate.
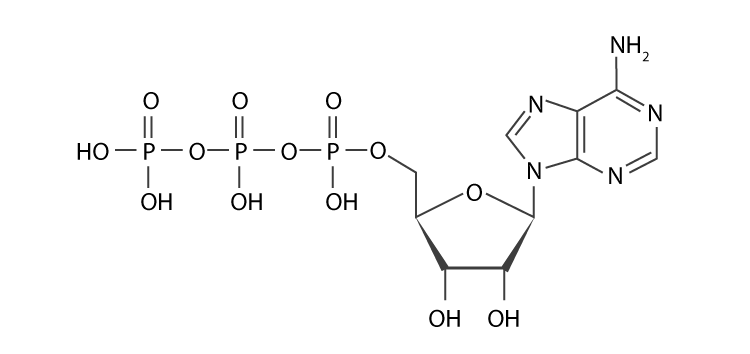
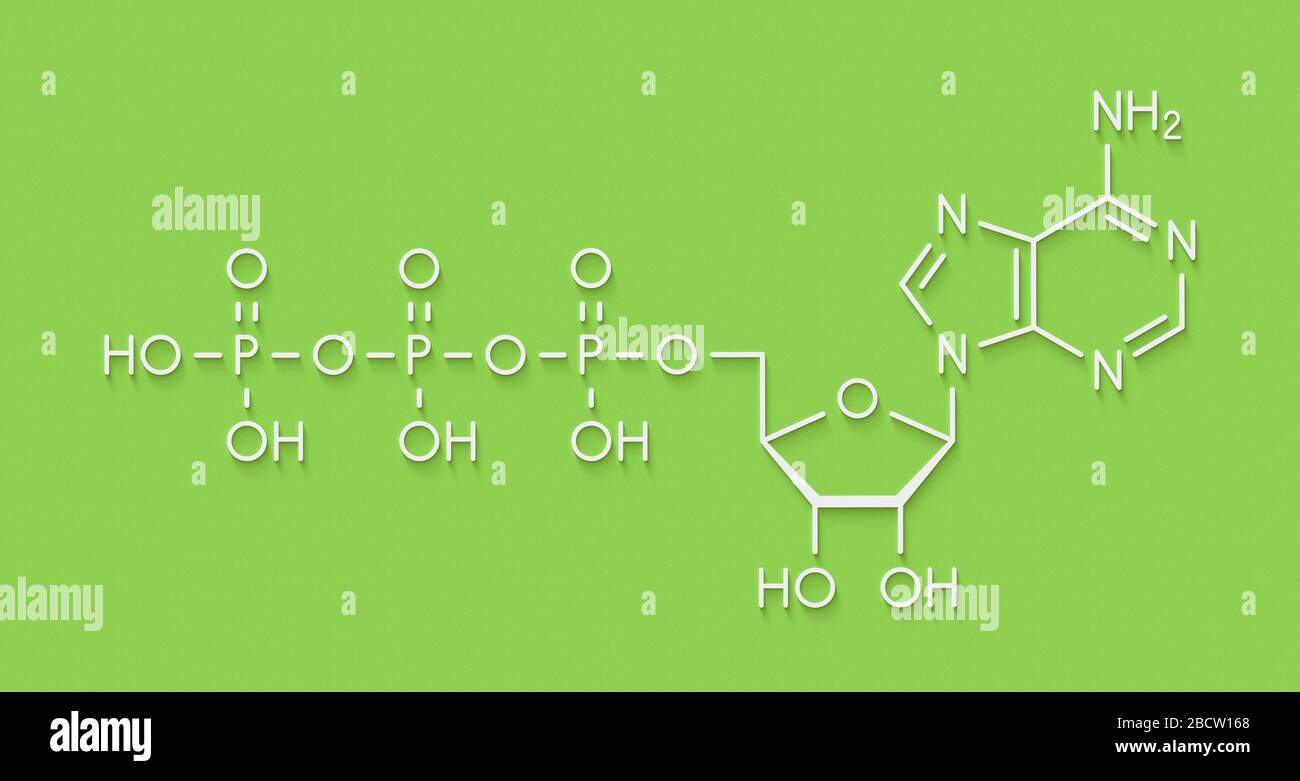
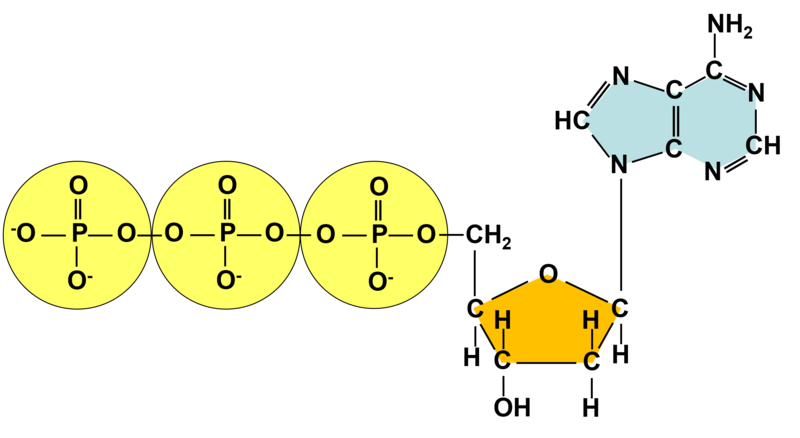
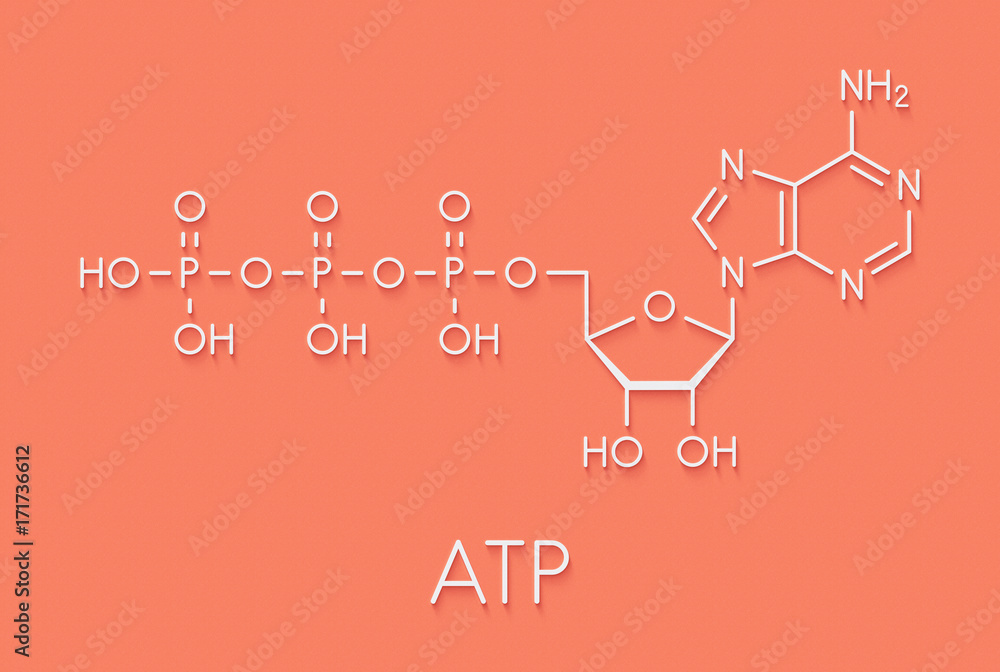
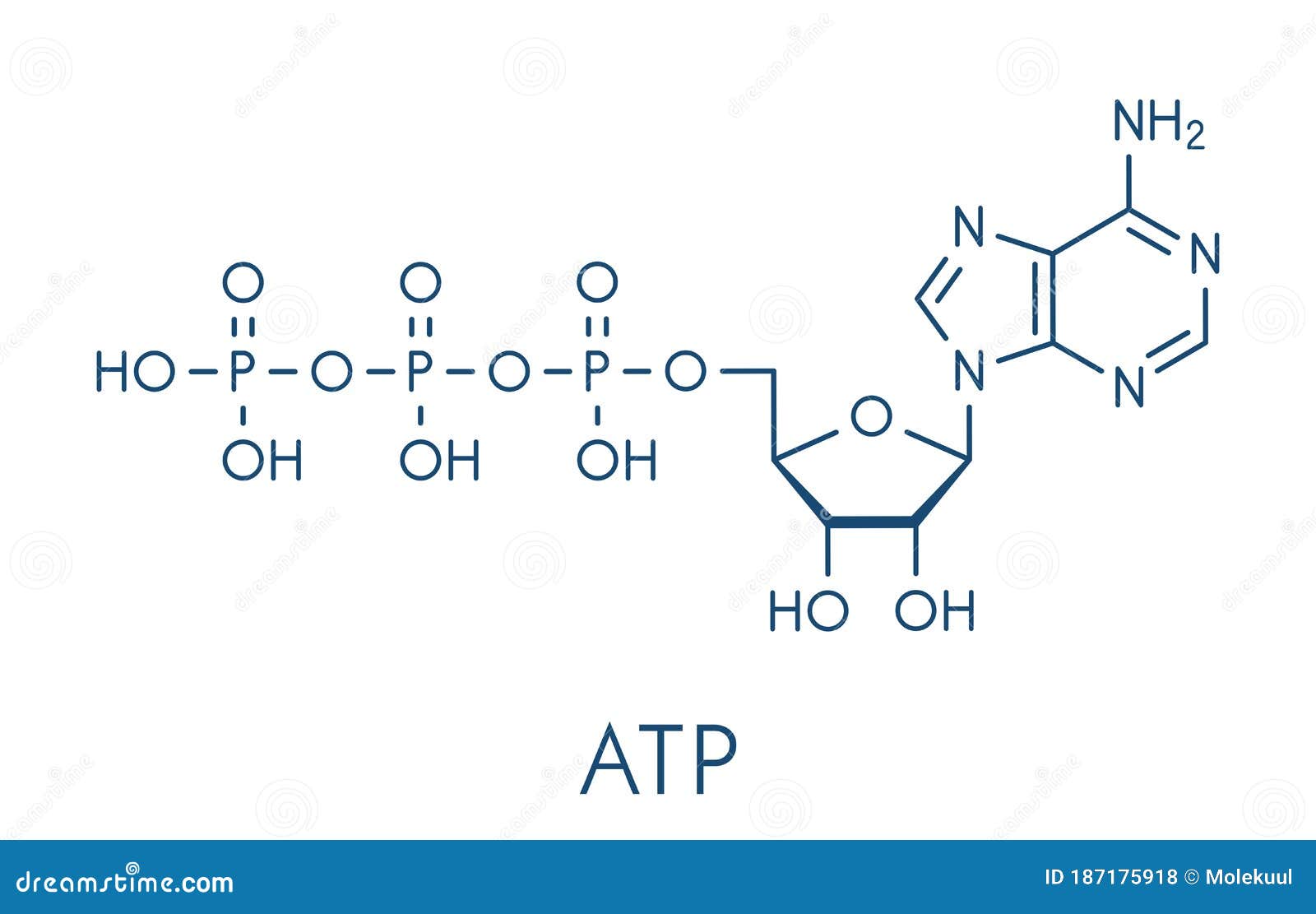
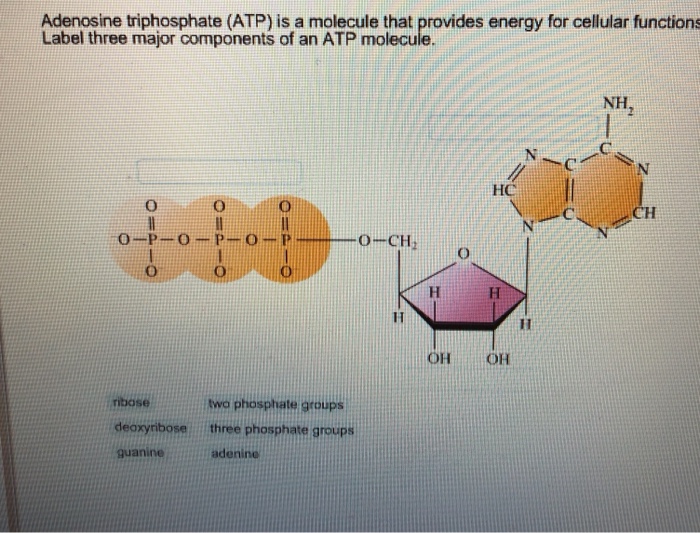
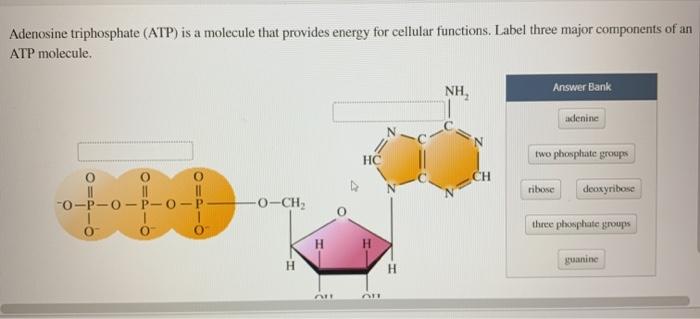
Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) is an organic compound and hydrotrope that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. PDF ATP and Energy: How do cells capture, store, and release energy? 1. Based on the model of the ATP molecule above, list the three parts of the ATP molecule and then label each on the simplified model of ATP shown below a. b. c. 2. The full name for an ATP molecule is Adenosine Triphosphate. Based on the model for ATP, what is meant by the "tri" in triphosphate? 3. Mastering Biology 5 Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the labels onto the table to indicate when each statement is true. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. 1. Orange dye moves independently of purple dye 2. Concentration gradients exist that drive diffusion of both dyes 3. There is a net movement of orange dye from side A to side B 4. Purple dye moves only from side B to ...
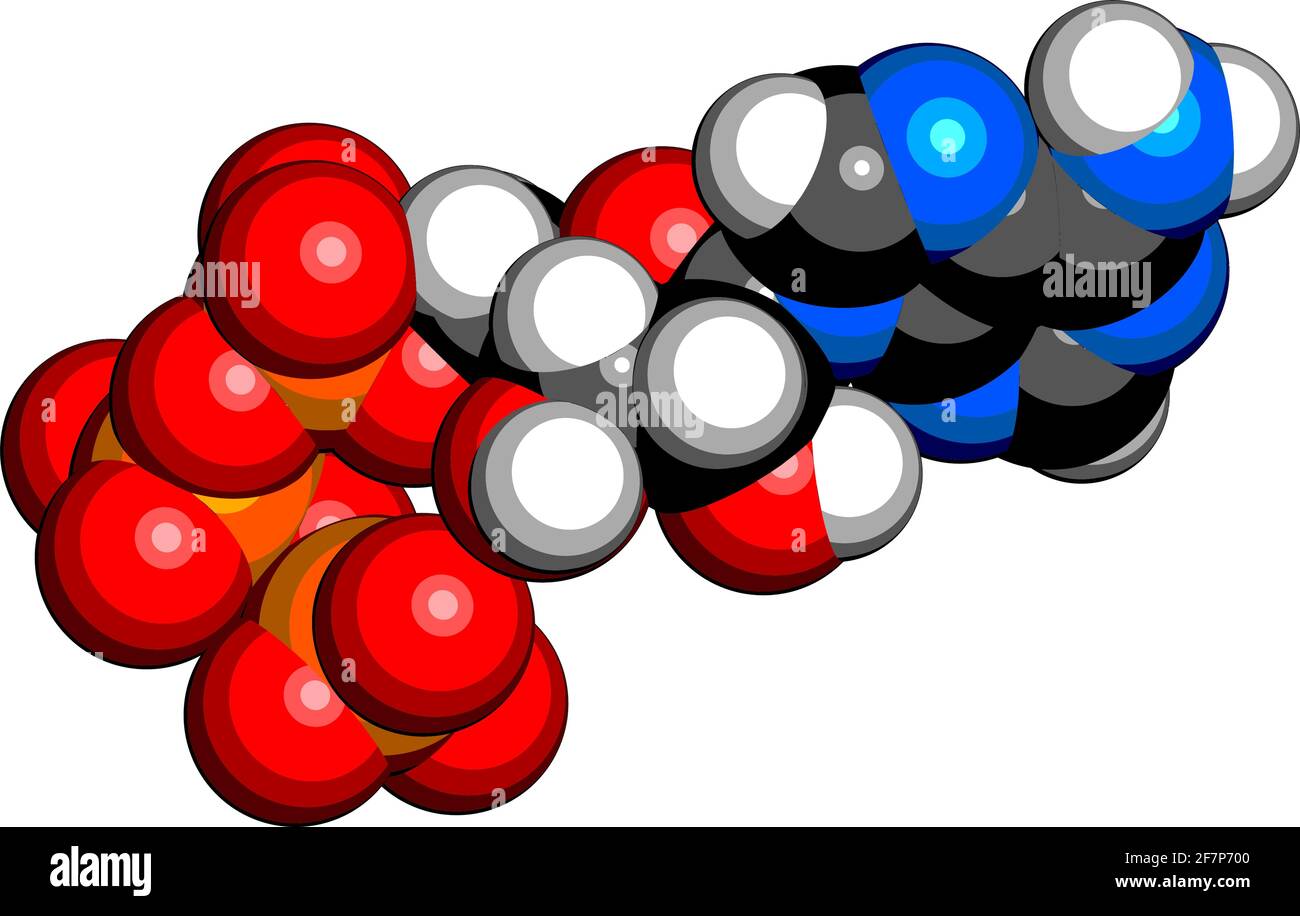
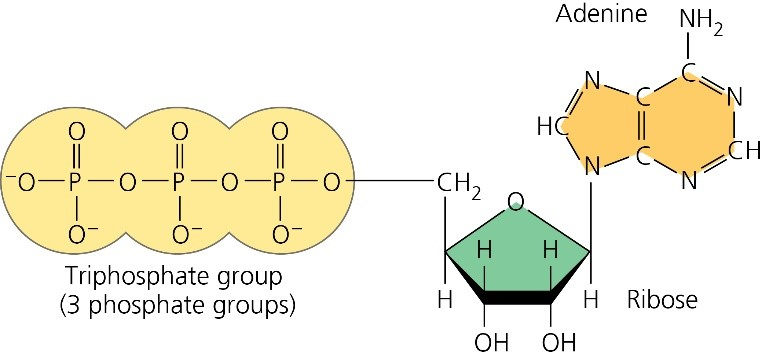
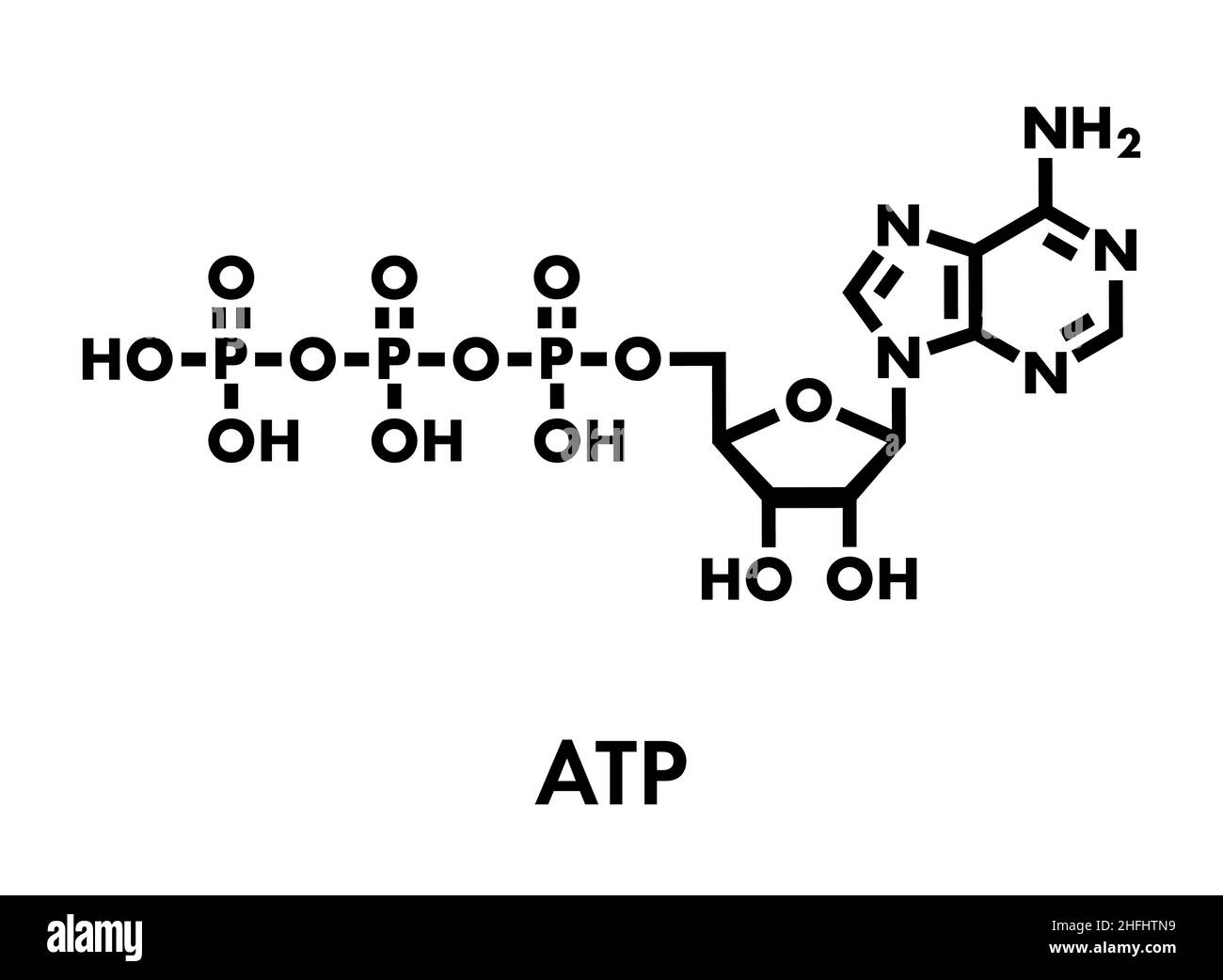
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules ATP consists of adenosine - composed of an adenine ring and a ribose sugar - and three phosphate groups (triphosphate). The phosphoryl groups, starting with the group closest to the ribose, are referred to as the alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) phosphates. Consequently, it is closely related to the adenine nucleotide, a monomer of RNA. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. Creatine Monohydrate | RYSE Supplements Size. Strength. Endurance. Creatine is stored in the muscle as creatine phosphate. Those familiar know ATP, cellular energy, is adenosine triphosphate. There’s something special about those phosphates. When they are clipped off the parent molecule, they release a ton of energy. The cell is able to harvest this energy a Piezo1 and Piezo2 Are Essential Components of Distinct ... - Science 02.09.2010 · Mechanotransduction, the conversion of mechanical force into biological signals, has crucial roles in physiology. In mammals, embryonic development, touch, pain, proprioception, hearing, adjustment of vascular tone and blood flow, flow sensing in kidney, lung growth and injury, bone and muscle homeostasis, as well as metastasis are all regulated by means of …
Photosynthesis Flashcards | Quizlet On diagram 5, fill in the labels with the following descriptions to show the connections between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. Left side, Top to bottom: ATP, ... The electron from a molecule of water goes with H+ to the ATP Synthase, to which it joins the sugar G3P.
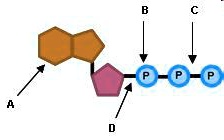
Р P- P 1. Label the ATP shown above. 2. Which part of the structure is ... The left side of the diagram is adenine, the middle part is ribose which is a sugar. A sugar molecule is composed of 12 carbon, 22 hydrogen, and 11 oxygen atoms that is made the structure of the sugar.. In ATP molecules, energy is stored in the covalent bonds that is present between phosphates.The greatest amount of energy is present in the bond between the second and third phosphate groups.
Answered: Complete and balance the following… | bartleby Q: The following molecule was formed by an intramolecular aldol reaction. Draw the dicarbonyl precursor… Draw the dicarbonyl precursor… A: Click to see the answer
DOC Read, Answer, Color, Label: Mitochondria - New Smyrna Beach High School Color and label the matrix (10) yellow on Figure 3. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar , and 3 phosphate groups ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells.
Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
Nucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group.With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the …
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace [34] Mutations have been found throughout the ATRX protein, with over 90% of them being located in the zinc finger and helicase domains. They also play an important role in sensing viral RNAs. Label each part of the atp molecule above in the spaces provided. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. How does atp differ from adp.
The Mitochondrion - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI ... In the mitochondria, the metabolism of sugars is completed, and the energy released is harnessed so efficiently that about 30 molecules of ATP are produced for each molecule of glucose oxidized. By contrast, only 2 molecules of ATP are produced per glucose molecule by glycolysis alone. Mitochondria can use both pyruvate and fatty acids as fuel.
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6.
ATP reading and coloring activity.pdf - Read, Answer, Color, Label ... Color and label the matrix (10) yellow on Figure 3. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by cells to do work. It is a nucleotide consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine), a 5-carbon sugar, and 3 phosphate groups. ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells.
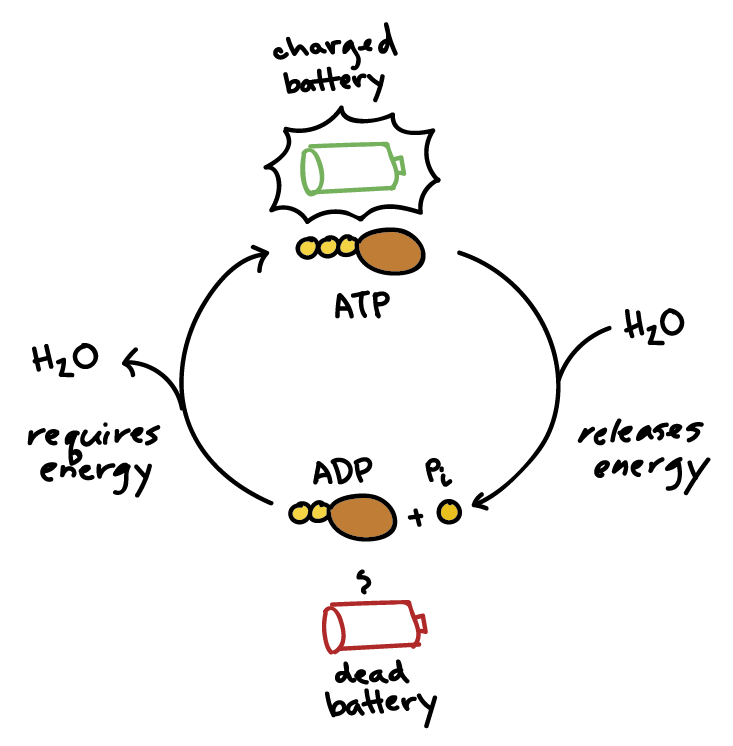
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule - Chegg 100% (1 rating) 7. From left to right- Adenine - Ribose - Phosphate groups 8. The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) … View the full answer Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule below.
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 - PubChem Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 | CID 5957 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological ...
Answered: Complete and balance the following… | bartleby Solution for Complete and balance the following molecular equations (indicate the relevant phase labels): LICI (s) + HSO4 (aq) → NH. (aq) + OH(aq) → AgNOs (aq)…
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: Answer link
2ATP: Crystal Structure Of A Cd8ab Heterodimer - National Center for ... Label Count Molecule; Proteins (3 molecules) A. 1: T-cell Surface Glycoprotein CD8 Alpha Chain. E. 1: Artifact Linker. B. 1: T-cell Surface Glycoprotein CD8 Beta Chain. Chemical and Non-standard biopolymers (1 molecule) 1: 1. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine * Click molecule labels to explore molecular sequence information.
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate | OpenStax Biology 2e - Lumen Learning ATP is the primary energy-supplying molecule for living cells. ATP is comprised of a nucleotide, a five-carbon sugar, and three phosphate groups. The bonds that connect the phosphates (phosphoanhydride bonds) have high-energy content. The energy released from ATP hydrolysis into ADP + P i performs cellular work.
Chapter 1: Acid–Base Reactions – OCLUE: Organic Chemistry, Life ... In the case of reactions that occur within aqueous solution, the H + is transferred to a water molecule to form H 3 O +. Consider, as an example, HCl; in aqueous solution HCl transfer a H + group to a water molecule. The products are H 3 O + (the conjugate acid of water) and Cl –, the conjugate base of HCl.
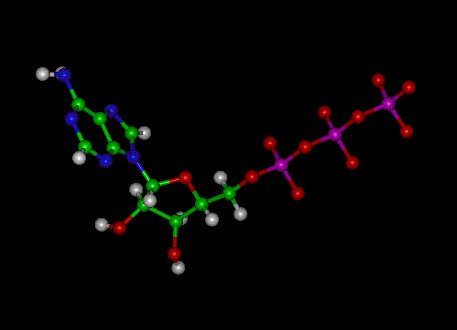
The ATP molecule in 3-D - BioTopics The ATP molecule - rotatable in 3 dimensions The ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule has 3 main parts: the base adenine - a double ring like section with several nitrogen atoms (blue), the 5 carbon sugar ribose in the centre, and 3 phosphate groups - a row of phosphorus atoms (orange) surrounded by oxygens (red).
atp molecule Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet Biological molecules, Enzyme, DNA, ATP. Polymerase. Monomers. Describe how glucose join form maltose. A large complex molecules composed by a long chain of monomers…. Are small repeat basic molecular unit, which form large molecu…. 1. two glucose combine remove water molecule,... 2. From between….
ATP Diagram | Quizlet a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di. two. ATP Cycle. a cycle that converts ADP into ATP & ATP releases energy and turns into ADP. Phosphate Group (removed) a phosphate is removed to release energy. Phosphate Group (added) A phosphate group is added using a small amount of energy.
ATP Molecule Structure: Fuel of Life - Indigo Instruments ATP was first discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann. Back then, it was considered that Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) was an energy source produced inside the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. Several years later in 1962, Geoffrey Burnstock discovered that it had the potential to carry messages between cells and that it helps in fighting human diseases.
Model of ATP Molecule | Perkins eLearning The model described is of a molecule of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the energy currency of the cell because it provides energy for the cell's activities. Understanding the structure of this molecule leads to a clear understanding of the manner in which it provides needed energy to the cell.
Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems.Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg 2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active.
Insights into the client protein release mechanism of the ATP 20.05.2022 · Spy is a cradle-shaped molecule with an overall positively charged, concave surface for binding to clients, whereas many clients, such as Im7, α-LA, and ADH, are overall negatively charged (Fig. 2a).
The Mitochondrion - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI … Mitochondria occupy a substantial portion of the cytoplasmic volume of eucaryotic cells, and they have been essential for the evolution of complex animals. Without mitochondria, present-day animal cells would be dependent on anaerobic glycolysis for all of their ATP. When glucose is converted to pyruvate by glycolysis, only a very small fraction of the total free energy …
ATP and ADP: Definition, Formation, Examples I ResearchTweet There are 3 phosphate molecule and one adenine molecule which forms the ATP. ATP to ADP Energy Release As the ATP molecule consist of 3phosphate molecule and an adenine molecule, thus when ATP is converted to ADP, a phosphate molecule is lost in this process. The reaction can be written as ATP → ADP + P i
ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College Usually the terminal phosphate is not simply removed, but instead is attached to another molecule. This process is known as phosphorylation. W + ATP -----> W~P + ADP where W is any compound, for example: glucose + ATP -----> glucose~P + ADP. Glucose can be converted into Glucose-6-phosphate by the addition of the phosphate group from ATP.
Photosynthesis Flashcards | Quizlet The electron from a molecule of water goes with H+ to the ATP Synthase, to which it joins the sugar G3P. Describe how ATP is produced in the light reactions. A electron goes through PSII then goes to the cytochrome complex then to PSI to which it goes to the ATP synthase.
How Does ADP Become ATP? Cycle, Structure, and Function - Study.com The molecular structure of ATP is comprised of: 1 adenine: A purine base. 1 ribose: A 5-carbon simple sugar. 3 phosphate molecules: The majority of the ATP's energy is also stored within its ...

















Post a Comment for "38 atp molecule with labels"