45 drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound.
Digestive Flashcards - Quizlet digestion is the breakdown large organic molecules into component parts that can be absorbed. carbohydrates are digested into (monosaccharides), protein into (amino acids), and triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol match the types of digestion with the correct description mechanical digestion- includes mastication and mixing food Chapter 17 digestive Flashcards - Easy Notecards Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. 20 Indicate where each enzyme (or its inactive precursor) is produced. 21 Classify each enzyme based on the substrate it decomposes. 22 The figures depict the stages of swallowing.
CH103 - Chapter 8: The Major Macromolecules - Chemistry 11.1 Introduction: The Four Major Macromolecules Within all lifeforms on Earth, from the tiniest bacterium to the giant sperm whale, there are four major classes of organic macromolecules that are always found and are essential to life. These are the carbohydrates, lipids (or fats), proteins, and nucleic acids.
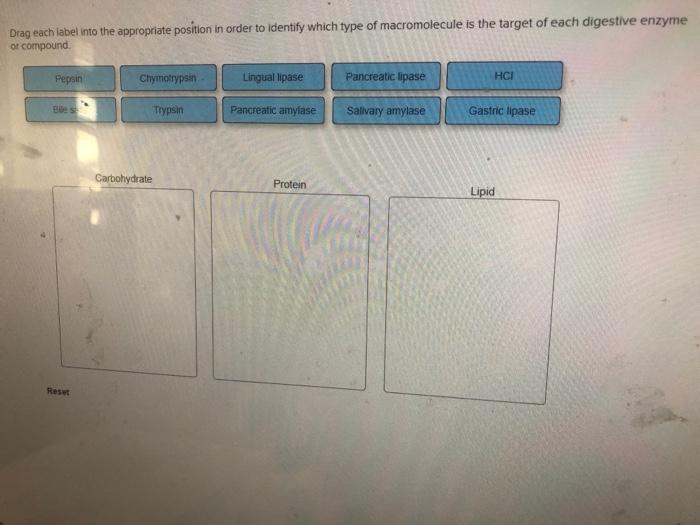
Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound.
9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands. (PDF) Sb1 model answers | Margaret Li - Academia.edu 4. (a) Protozoan (any one of): Amoeba, Paramecium (b) In Paramecium, a food vacuole develops at the end 8. (a) Water will move into the cell and it will burst (lyse). of the oral groove and is pinched off to circulate (b) The cell would lose water and the plasma within the cell. LookWAYup definition of - senses, usage, synonyms, thesaurus. Online Dictionaries: Definition of Options|Tips
Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound.. (PDF) Principles and Techiniques of ... - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. A&P Ch 17 Digestive Homework Flashcards - Quizlet The root canal of a tooth contains gingiva. blood vessels and nerves. cementum. dentin. blood vessels and nerves. Anatomy of stomach and oral cavity Identify whether the structures are associated with the oral cavity or the stomach by dragging each label into the appropriate position. Oral: Bicuspids Uvula Salivary ducts Papillae Soft palate Expat Dating in Germany - chatting and dating - Front page DE Expatica is the international community’s online home away from home. A must-read for English-speaking expatriates and internationals across Europe, Expatica provides a tailored local news service and essential information on living, working, and moving to your country of choice. AP Biology - CourseNotes 3 reactions changing glucose into a compound that can be readily cleaved into 3-carbon phosphorylated molecules; 2 of the reactions require use of ATP; step B - cleavage/rearrangement 2 reactions break up 6-carbon molecule into 2 3-carbon molecules; 1st of 2 reactions forms G3P and another molecule that turns into G3P through the 2nd reaction
drag each label into the appropriate position in | Chegg.com Al rights reser 9 each tabel Into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound Lipid Protein Carbohydrate Trypin Pancreatic Swamy Unge Pancreatice HC Chymotrypsin Boat Gait Drag and drop then you can the comediwhen the box when it shoulder Solved Drag each label into the appropriate position in - Chegg question: drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound gastric lipase pancreatic amylase lactase lecithin carboxypeptidase salivary amylase dipeptidase maltase pancreatic lipaso lingual lipase aminopeptidase sucrase dextrinase bile salts trypsin … A & P Lab Assignment Flashcards | Quizlet Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. carbohydrate: salivary amylase, dextrinase, maltase, lactase, pancreatic amylase, glucoamylase, sucrase, 3.1 The Cell Membrane - Anatomy & Physiology A glycoprotein is a protein that has carbohydrate molecules attached, which extend into the extracellular environment. The attached carbohydrate tags on glycoproteins aid in cell recognition. The carbohydrates that extend from membrane proteins and even from some membrane lipids collectively form the glycocalyx.
Cell Structure | SEER Training For descriptive purposes, the concept of a "generalized cell" is introduced. It includes features from all cell types. A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct ... Enzymes and the active site (article) | Khan Academy The answer depends on the enzyme. Some enzymes speed up chemical reactions by bringing two substrates together in the right orientation. Others create an environment inside the active site that's favorable to the reaction (for instance, one that's slightly acidic or non-polar). Solved > Drag each label into the appropriate position in ... - ScholarOn Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. Solution 5 (1 Ratings ) BIO23 F19-S20 Complete Course Guide by Human Anatomy - Issuu List each type of bond in order by relative strength. b. Explain the mechanism of each type of bond. c. Provide biologically significant examples of each. ... Draw and label each of the functional ...
Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify ... Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify where each secretion enters the GI tract. Complete each sentence by dragging the proper label into the appropriate position.Then, re-arrange the sentences into a logical order of digestive processes. Complete each sentence by dragging the proper label into the correct position.
Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to id +1 (347) 474-1028 info@essayparlour.com Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to id Academic Writing Biology Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to id Approximately 275 words/page All paper formats (APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago/Turabian) 0% plagiarism rate Free revisions within a 30 day period
Post a Comment for "45 drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound."